篇首语:本文由编程笔记#小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++ 实战之OpenCL环境搭建相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
接触opencl并行计算变成之前,在我的认知观中,所谓的并行应该就是应用多线程技术达到,比如openMP,openMPI等多线程技术。不过这些都是在cpu上运行,原理都是更好的利用多核处理器的硬件特性,让程序最大程度的利用了多核的优势。
接触opencl之后,认识到了opencl编程技术可以把一些复杂的代码搬运到GPU或其他加速处理器上运行,而gpu又比cpu更适应与计算比如加法,乘法等。第一感觉想到的就是opengl里面的shader,编写shader不就是把渲染相关的代码放在gpu上运行吗?其实,普通的算法代码也可以放在gpu上运行,而opencl就是实现这一技术的标准。
花了一两周时间对opencl进行了一个多方面粗略的了解,opencl更加接近于硬件,所以有很多硬件相关的概念,比如平台结构,内存模型等,还涉及到各种指令操作,对于一开始准备学习opencl的软件开发人员来说比较生涩难懂,所以前阶段会跳过对这些硬件相关的概念的钻研,重心转移到如何用opencl标准接口编程和opencl的编程模型,软件架构等。
OpenCL的一个最大的优势,就是他的跨平台性,首先不同的操作系统mac,windows,android;其次不同的cpu,gpu也都支持。我目前在mac上进行opencl的开发学习,支持的版本是opencl1.2.也会在手机上进行测试,不同的硬件厂商他们都会自己实现相应的opencl库,而头文件都是标准的。
编程的IDE是mac自带的xcode,mac系统里面已经集成了opencl的sdk所以不需要去另外去下载了,只要在工程中把它加进来就可以进行opencl开发了,很方便。
下面时mac环境搭建过程,比较简单,另外目前mac最高支持opencl1.2。

点击+按钮,开始选择opencl库,直接搜索opencl就会出现,如下:
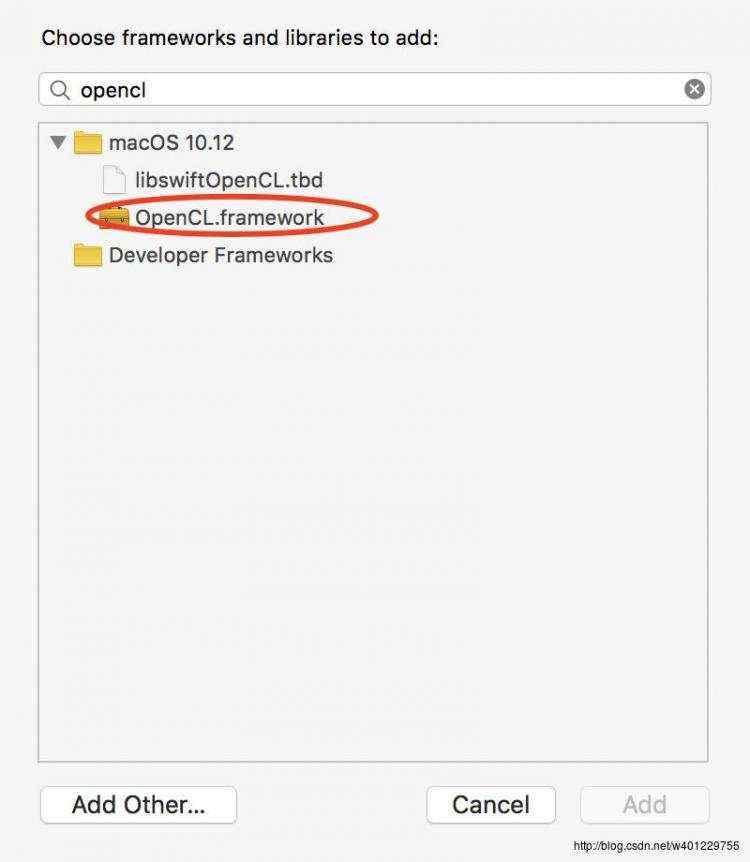
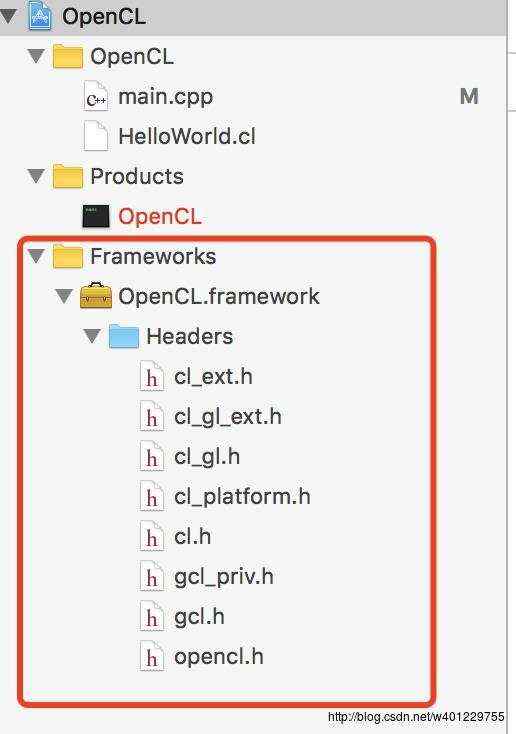
添加之后,工程项目就会多一个opencl的framework :
opencl开发有这几个标准的接口流程:
1.获取平台信息:
clGetPlatformIDs(1, &firstPlatformId, &numPlatforms);
2.创建上下文:
clCreateContextFromType(contextProperties, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,
NULL, NULL, &errNum);
3.获取设备缓冲区大小
clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, 0, NULL, &deviceBufferSize);
4.为设备分配缓存
clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, deviceBufferSize, devices, NULL);
5.选取可用的设备中的一个:
clCreateCommandQueue(context, devices[0], 0, NULL);
6.创建kernel对象和编译源代码
program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1,
(const char**)&srcStr,
NULL, NULL);
errNum = clBuildProgram(program, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
7.最后释放opencl资源
下面是在mac上跑的例子:
//
// main.cpp
// OpenCL
//
// Created by xxx on 2017/9/19.
// Copyright © 2017年 xxx. All rights reserved.
//
#include
#include <iostream>
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
const int ARRAY_SIZE &#61; 100000;
//一、 选择OpenCL平台并创建一个上下文
cl_context CreateContext()
cl_int errNum;
cl_uint numPlatforms;
cl_platform_id firstPlatformId;
cl_context context &#61; NULL;
//选择可用的平台中的第一个
errNum &#61; clGetPlatformIDs(1, &firstPlatformId, &numPlatforms);
if (errNum !&#61; CL_SUCCESS || numPlatforms <&#61; 0)
std::cerr <<"Failed to find any OpenCL platforms." <<std::endl;
return NULL;
//创建一个OpenCL上下文环境
cl_context_properties contextProperties[] &#61;
CL_CONTEXT_PLATFORM,
(cl_context_properties)firstPlatformId,
0
;
context &#61; clCreateContextFromType(contextProperties, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,
NULL, NULL, &errNum);
return context;
//二、 创建设备并创建命令队列
cl_command_queue CreateCommandQueue(cl_context context, cl_device_id *device)
cl_int errNum;
cl_device_id *devices;
cl_command_queue commandQueue &#61; NULL;
size_t deviceBufferSize &#61; -1;
// 获取设备缓冲区大小
errNum &#61; clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, 0, NULL, &deviceBufferSize);
if (deviceBufferSize <&#61; 0)
std::cerr <<"No devices available.";
return NULL;
// 为设备分配缓存空间
devices &#61; new cl_device_id[deviceBufferSize / sizeof(cl_device_id)];
errNum &#61; clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, deviceBufferSize, devices, NULL);
//选取可用设备中的第一个
commandQueue &#61; clCreateCommandQueue(context, devices[0], 0, NULL);
*device &#61; devices[0];
delete[] devices;
return commandQueue;
// 三、创建和构建程序对象
cl_program CreateProgram(cl_context context, cl_device_id device, const char* fileName)
cl_int errNum;
cl_program program;
std::ifstream kernelFile(fileName, std::ios::in);
if (!kernelFile.is_open())
std::cerr <<"Failed to open file for reading: " <
return NULL;
std::ostringstream oss;
oss <
const char *srcStr &#61; srcStdStr.c_str();
program &#61; clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1,
(const char**)&srcStr,
NULL, NULL);
errNum &#61; clBuildProgram(program, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
return program;
//创建和构建程序对象
bool CreateMemObjects(cl_context context, cl_mem memObjects[3],
float *a, float *b)
memObjects[0] &#61; clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE, a, NULL);
memObjects[1] &#61; clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE, b, NULL);
memObjects[2] &#61; clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE, NULL, NULL);
return true;
// 释放OpenCL资源
void Cleanup(cl_context context, cl_command_queue commandQueue,
cl_program program, cl_kernel kernel, cl_mem memObjects[3])
for (int i &#61; 0; i <3; i&#43;&#43;)
if (memObjects[i] !&#61; 0)
clReleaseMemObject(memObjects[i]);
if (commandQueue !&#61; 0)
clReleaseCommandQueue(commandQueue);
if (kernel !&#61; 0)
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
if (program !&#61; 0)
clReleaseProgram(program);
if (context !&#61; 0)
clReleaseContext(context);
int main(int argc, char** argv)
cl_context context &#61; 0;
cl_command_queue commandQueue &#61; 0;
cl_program program &#61; 0;
cl_device_id device &#61; 0;
cl_kernel kernel &#61; 0;
cl_mem memObjects[3] &#61; 0, 0, 0 ;
cl_int errNum;
// uint64_t t1,t2,t3;
clock_t t1,t2,t3;
const char* filename &#61; "/Users/xxxxx/Projects/OpenCL/OpenCL/HelloWorld.cl";
// 一、选择OpenCL平台并创建一个上下文
context &#61; CreateContext();
// 二、 创建设备并创建命令队列
commandQueue &#61; CreateCommandQueue(context, &device);
//创建和构建程序对象
program &#61; CreateProgram(context, device, filename);//"HelloWorld.cl");
// 四、 创建OpenCL内核并分配内存空间
kernel &#61; clCreateKernel(program, "hello_kernel", NULL);
//创建要处理的数据
float result[ARRAY_SIZE];
float a[ARRAY_SIZE];
float b[ARRAY_SIZE];
for (int i &#61; 0; i
a[i] &#61; (float)i;
b[i] &#61; (float)(ARRAY_SIZE - i);
t1 &#61; clock(); //mach_absolute_time();
printf("t1 &#61; %.8f\\n",(double)t1);
for(int j &#61; 0;j
t2 &#61; clock(); //mach_absolute_time();
printf("t2 &#61; %.8f\\n",(double)t2);
//创建内存对象
if (!CreateMemObjects(context, memObjects, a, b))
Cleanup(context, commandQueue, program, kernel, memObjects);
return 1;
// 五、 设置内核数据并执行内核
errNum &#61; clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[0]);
errNum |&#61; clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[1]);
errNum |&#61; clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[2]);
size_t globalWorkSize[1] &#61; ARRAY_SIZE ;
size_t localWorkSize[1] &#61; 1 ;
errNum &#61; clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(commandQueue, kernel, 1, NULL,
globalWorkSize, localWorkSize,
0, NULL, NULL);
// 六、 读取执行结果并释放OpenCL资源
errNum &#61; clEnqueueReadBuffer(commandQueue, memObjects[2], CL_TRUE,
0, ARRAY_SIZE * sizeof(float), result,
0, NULL, NULL);
t3 &#61; clock(); //mach_absolute_time();
printf("cpu t &#61; %.8f\\n",(float)(t2-t1)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
printf("gpu t &#61; %.8f \\n",(double)(t3-t2)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
//std::cout<<"the noemal delta is &#61; "<
// std::cout<<"the opencl delta is &#61; "<<(t3-t2)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<
// for (int i &#61; 0; i
//
// std::cout <
//
std::cout <<std::endl;
std::cout <<"Executed program succesfully." <<std::endl;
getchar();
Cleanup(context, commandQueue, program, kernel, memObjects);
return 0;
下面是kernel 源文件&#xff1a;
__kernel void hello_kernel(__global const float *a,
__global const float *b,
__global float *result)
int gid &#61; get_global_id(0);
result[gid] &#61; a[gid] &#43; b[gid];
下面是在macbook pro 上的运行结果&#xff1a;
t1 &#61; 143206.00000000
t2 &#61; 143562.00000000
cpu t &#61; 0.00035600
gpu t &#61; 0.00155900
Executed program succesfully.
看这个结果是cpu耗时更短&#xff0c;这个在情理之中&#xff0c;随着维数和计算量增大&#xff0c;gpu的优势才会体现&#xff0c;后面会逐步证明。
github地址&#xff1a;https://github.com/myhouselove/mac-opencl
我用android studio 2.2以上的版本搭建的ndk & cmake native工程开发学习opencl&#xff1a;
下面是搭建过程&#xff1a;
1.按照网上所说新建一个cmake的android工程&#xff0c;具体可以百度一下&#xff0c;这里是我的另外一篇博客的介绍&#xff1a;http://blog.csdn.net/w401229755/article/details/75810028
然后最重要的部分就是找到具体手机的opencl sdk和标准的头文件。我用的小米4 &#xff0c;他的sdk就在/system/vendor/lib/libOpenCL.so下。我把他pull出来放在android工程中使用。
配置cmakelist.txt
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.4.1)
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
set(CMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE on)
set(libs "$CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR/src/main/jniLibs")
include_directories($CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR/src/main/cpp/include)
#--------------------------------------------------- import ---------------------------------------------------#
add_library(libOpenCL SHARED IMPORTED )
set_target_properties(libOpenCL PROPERTIES
IMPORTED_LOCATION "$libs/$ANDROID_ABI/libOpenCL.so")
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
native-lib
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
src/main/cpp/native-lib.cpp )
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
native-lib libOpenCL
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
$log-lib )
下面是c&#43;&#43;的源代码&#xff1a;
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define TAG OpenCL
#define LOGD(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_DEBUG,"OPENCL",__VA_ARGS__)
const int ARRAY_SIZE &#61; 100000;
//一、 选择OpenCL平台并创建一个上下文
cl_context CreateContext()
cl_int errNum;
cl_uint numPlatforms;
cl_platform_id firstPlatformId;
cl_context context &#61; NULL;
//选择可用的平台中的第一个
errNum &#61; clGetPlatformIDs(1, &firstPlatformId, &numPlatforms);
if (errNum !&#61; CL_SUCCESS || numPlatforms <&#61; 0)
std::cerr <<"Failed to find any OpenCL platforms." <<std::endl;
return NULL;
//创建一个OpenCL上下文环境
cl_context_properties contextProperties[] &#61;
CL_CONTEXT_PLATFORM,
(cl_context_properties)firstPlatformId,
0
;
context &#61; clCreateContextFromType(contextProperties, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,
NULL, NULL, &errNum);
return context;
//二、 创建设备并创建命令队列
cl_command_queue CreateCommandQueue(cl_context context, cl_device_id *device)
cl_int errNum;
cl_device_id *devices;
cl_command_queue commandQueue &#61; NULL;
size_t deviceBufferSize &#61; -1;
// 获取设备缓冲区大小
errNum &#61; clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, 0, NULL, &deviceBufferSize);
if (deviceBufferSize <&#61; 0)
std::cerr <<"No devices available.";
return NULL;
// 为设备分配缓存空间
devices &#61; new cl_device_id[deviceBufferSize / sizeof(cl_device_id)];
errNum &#61; clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, deviceBufferSize, devices, NULL);
//选取可用设备中的第一个
commandQueue &#61; clCreateCommandQueue(context, devices[0], 0, NULL);
*device &#61; devices[0];
delete[] devices;
return commandQueue;
// 三、创建和构建程序对象
cl_program CreateProgram(cl_context context, cl_device_id device, const char* fileName)
cl_int errNum;
cl_program program;
std::ifstream kernelFile(fileName, std::ios::in);
if (!kernelFile.is_open())
LOGD("Failed to open file for reading: %s\\n" , fileName );
return NULL;
std::ostringstream oss;
oss <
const char *srcStr &#61; srcStdStr.c_str();
program &#61; clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1,
(const char**)&srcStr,
NULL, NULL);
errNum &#61; clBuildProgram(program, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
return program;
//创建和构建程序对象
bool CreateMemObjects(cl_context context, cl_mem memObjects[3],
float *a, float *b)
memObjects[0] &#61; clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE, a, NULL);
memObjects[1] &#61; clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE, b, NULL);
memObjects[2] &#61; clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE, NULL, NULL);
return true;
// 释放OpenCL资源
void Cleanup(cl_context context, cl_command_queue commandQueue,
cl_program program, cl_kernel kernel, cl_mem memObjects[3])
for (int i &#61; 0; i <3; i&#43;&#43;)
if (memObjects[i] !&#61; 0)
clReleaseMemObject(memObjects[i]);
if (commandQueue !&#61; 0)
clReleaseCommandQueue(commandQueue);
if (kernel !&#61; 0)
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
if (program !&#61; 0)
clReleaseProgram(program);
if (context !&#61; 0)
clReleaseContext(context);
int test()
cl_context context &#61; 0;
cl_command_queue commandQueue &#61; 0;
cl_program program &#61; 0;
cl_device_id device &#61; 0;
cl_kernel kernel &#61; 0;
cl_mem memObjects[3] &#61; 0, 0, 0 ;
cl_int errNum;
// uint64_t t1,t2,t3;
clock_t t1,t2,t3;
const char* filename &#61; "HelloWorld.cl";
// 一、选择OpenCL平台并创建一个上下文
context &#61; CreateContext();
// 二、 创建设备并创建命令队列
commandQueue &#61; CreateCommandQueue(context, &device);
//创建和构建程序对象
program &#61; CreateProgram(context, device, filename);//"HelloWorld.cl");
// 四、 创建OpenCL内核并分配内存空间
kernel &#61; clCreateKernel(program, "hello_kernel", NULL);
//创建要处理的数据
float result[ARRAY_SIZE];
float a[ARRAY_SIZE];
float b[ARRAY_SIZE];
for (int i &#61; 0; i
a[i] &#61; (float)i;
b[i] &#61; (float)(ARRAY_SIZE - i);
t1 &#61; clock(); //mach_absolute_time();
LOGD("t1 &#61; %.8f\\n",(double)t1);
for(int j &#61; 0;j
t2 &#61; clock(); //mach_absolute_time();
LOGD("t2 &#61; %.8f\\n",(double)t2);
//创建内存对象
if (!CreateMemObjects(context, memObjects, a, b))
Cleanup(context, commandQueue, program, kernel, memObjects);
return 1;
// 五、 设置内核数据并执行内核
errNum &#61; clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[0]);
errNum |&#61; clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[1]);
errNum |&#61; clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[2]);
size_t globalWorkSize[1] &#61; ARRAY_SIZE ;
size_t localWorkSize[1] &#61; 1 ;
errNum &#61; clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(commandQueue, kernel, 1, NULL,
globalWorkSize, localWorkSize,
0, NULL, NULL);
// 六、 读取执行结果并释放OpenCL资源
errNum &#61; clEnqueueReadBuffer(commandQueue, memObjects[2], CL_TRUE,
0, ARRAY_SIZE * sizeof(float), result,
0, NULL, NULL);
t3 &#61; clock(); //mach_absolute_time();
LOGD("cpu t &#61; %.8f\\n",(float)(t2-t1)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
LOGD("gpu t &#61; %.8f \\n",(double)(t3-t2)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
LOGD("Executed program succesfully.");
getchar();
Cleanup(context, commandQueue, program, kernel, memObjects);
return 0;
extern "C"
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_wangmingyong_opencl_MainActivity_stringFromJNI(
JNIEnv *env,
jobject /* this */)
test();
std::string hello &#61; "Hello from C&#43;&#43;";
return env->NewStringUTF(hello.c_str());
记得添加cl文件&#xff0c;这边cl文件跟上面mac中的cl一样。
具体代码可以看一下github 地址&#xff1a;https://github.com/myhouselove/OpenCL-android
上面分别是opencl在mac和android上面的初步简单应用&#xff0c;属于很简单的开发环境入门&#xff0c;证明opencl的跨平台性还是很强的&#xff0c;同样的代码基本不要做什么修改&#xff0c;后续会结合opencv的一些矩阵算法&#xff0c;具体学习分析一下opencl的编程和性能方面的知识点。

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有